The main cause of acute knee pain in patients over 50 years of age is gonarthrosis (deforming arthrosis of the knee joint).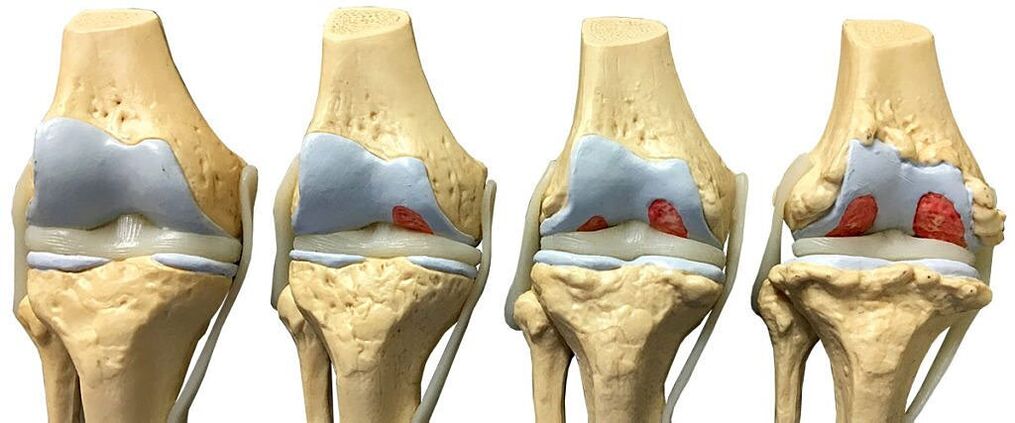 The disease is characterized by rapid progression, can cause disability and incapacity for work, so timely recognition of symptoms of knee arthrosis and treatment of the disease, including at home, is a major task in the study of patients at pathological risk. the musculoskeletal system.
The disease is characterized by rapid progression, can cause disability and incapacity for work, so timely recognition of symptoms of knee arthrosis and treatment of the disease, including at home, is a major task in the study of patients at pathological risk. the musculoskeletal system.
What is knee osteoarthritis
The knee joint is one of the most mobile joints in the human skeleton, prone to injuries and other mechanical injuries. It connects the tibia and femur and the largest sesame bone found in the tendons of the four-headed femoris (patella or patella). The surfaces of the joint are covered with cartilage tissue - a dense, flexible material that surrounds the chondrocytes (oval cells formed from chondroblasts) and creates a protective sheath around them, as well as acting as a shock absorber.
The composition of cartilage contains collagen - a fibrillar protein that is a major component of connective fibers and provides cartilage strength and elasticity - and glucosamine. Glucosamine is a substance produced by cartilage. Glucosamine is part of the synovial fluid - a yellowish, flexible mass that fills the joint cavity and acts as a lubricant. When the synthesis of glucosamine and proteoglycans is impaired, the amount of synovial fluid decreases, leading to exposure of parts of the joint and the development of severe pain, and therefore treatment of grade I arthrosis of the knee joint is always included. use of chondroprotective drugs.
What happens in the joints in arthrosis:
- the cartilage becomes soft and loose, with deep ulcers on its surface;
- the joint membrane thickens;
- the composition of the synovial fluid changes, its secretion decreases;
- there is a twitching of the ligaments and the joint sheath;
- the joint cavity is filled with secretions - an inflammatory fluid that is released from the blood vessels during the period of acute inflammation.
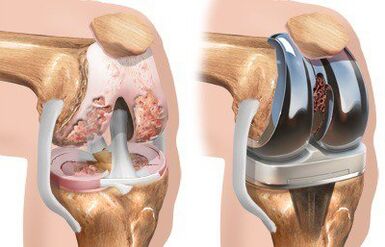
In time and without proper treatment, arthrosis leads to complete deformity and destruction of the knee joint, while the patient may also show unnatural mobility and complete immobility of the joint. In case of diagnosed arthrosis of the knee joint, the doctor may recommend joint surgery - a surgical procedure to replace the injured joint with an artificial prosthesis of the right size - to stop the destruction of the joint and cartilage surface.
The cost of primary knee joint surgery varies by region and can range from $ 255 to $ 1, 465.
If there are indications, the operation can be performed according to the quota within the CHI program.
Classification and etiological factors
Arthrosis of the knee joint may be primary or secondary. Primary arthrosis is diagnosed in cases where it is impossible to determine the exact cause of the pathology. If the cartilage deformity was preceded by other diseases and pathologies, knee injuries, arthrosis is considered secondary, ie it develops in the background of the primary disease.
The main causes of secondary arthrosis of the knee joints are:
- various dysplasias and other pathologies in which abnormal tissue development and formation occurs;
- neurodstrophic disorders of the lumbar or cervical spine;
- inflammation of the knee joint (arthritis);
- joint injuries and microtraumas;
- surgical removal of the damaged meniscus or part of it (meniscectomy);
- diseases of the endocrine system and hormonal disorders in which the rate of metabolic reactions is slowed down, the metabolism in the bone tissue is disrupted.
Primary arthrosis of the knee joint often develops in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle or, conversely, in those who regularly experience increased physical activity in the knee joint. Overweight patients over the age of 50, residents of environmentally unfavorable areas, and patients with various toxic substances (smokers, drug addicts, alcoholics) are also at increased risk of developing gonarthrosis.
Regular hypothermia can contribute to inflammation and further deformity of the knee joint, so people prone to musculoskeletal disorders are advised to adhere to the temperature system and to stop activities related to prolonged low temperature exposure (outdoor work, refrigeration and freezing), etc. ). d. ).
Women over the age of 45 who are interested in the treatment of knee arthrosis should be aware that the reduction in estrogen synthesis that may occur after menopause and in some gynecological diseases may be a provocative factor in the development of pathology: endometrial hyperplasia, uterine myoma. Another negative factor is the variety of diets that limit the intake of foods rich in minerals, vitamins and other elements necessary for joint health.
signs and symptoms
In order to have the best possible prognosis for later life, it is necessary to know not only how to treat knee arthrosis, but also what the symptoms of the disease are. This is necessary for timely access to a specialist and early detection of possible deformities and other injuries to the knee joint. In the initial stage, the pathology has relatively few symptoms, so grade 1 knee arthrosis can only be identified after hardware and instrumental diagnosis.
The first symptoms of the disease are:
- morning stiffness in the knee;
- pain while walking when walking more than 1-1, 5 km;
- knee pain with prolonged sitting (more than 2 hours in a row);
- pain in the knee joint after prolonged standing;
- knee pain that occurs at the end of the day or in the first half of sleep at night.
If the patient does not receive the necessary treatment at this stage, the disease will progress. To select a drug suitable for knee arthrosis, a series of diagnostic tests (MRI, computed tomography, radiography, etc. ) should be performed and the degree of deformation and the level of synovial fluid should be determined. cavity, cartilage tissue, and joint membrane density. The symptoms of 2 and 3 degree arthrosis of the knee are shown in the table below.
| diagnostic sign | Arthrosis of the knee is 2 degrees | Arthrosis of the knee is 3 degrees |
|---|---|---|
| Pain during night rest | It may occur when changing posture or getting out of bed. | It happens without movement. |
| Possibility to use public transport (except for low-floor buses) | The patient feels pain when climbing the stairs, but with some restrictions, he can use public transportation without assistance. | Due to the limited mobility of the knee joint, the patient cannot get on the bus or tram on his own. |
| Lameness | Expressed a little. | Lameness is strongly expressed, additional supports (sticks) are needed for movement. |
| Stiffness in the knee after waking up | It lasts less than 10-15 minutes. | It lasts for about 20-30 minutes or more. |
| Pain while walking | Occurs after passing 800-1000 m. | They start at the beginning of the movement and increase after covering a distance of less than 500 m. |
| Self-service capability | Usually saved. | The patient cannot perform many activities without outside help. |
Treatment of knee arthrosis at home
Knee arthrosis can be treated with:
- medical methods;
- physiotherapy exercises;
- massage.
The use of prescriptions for traditional medicine is only possible after consultation with your doctor and is not a substitute for the main treatment prescribed by a specialist.
The choice of drugs and methods of treatment depends not only on the age and chronic diseases of the patient, but also on the stage of arthrosis and the degree of deformity of the cartilage and joint surface.
Arthrosis 1 degree
This is the mildest form of arthrosis, which in most cases can be cured with minor medication and additional measures: massage, gymnastics, physiotherapy. The most effective treatment for knee inflammation, regardless of its stage, is laser therapy. This is the main method of physiotherapy that gives quite good results in the early stages of arthrosis.
It helps to achieve the following effect:
- the degree of inflammation in the joint cavity decreases;
- the intensity of the pain decreases;
- stimulate the process of tissue regeneration;
- the need for glucocorticosteroids and other drugs with serious side effects is eliminated.
As an alternative to laser therapy, your doctor may offer pulse magnetotherapy, acupuncture, electromyostimulation, and electrophoresis.
All of these methods are quite effective in treating arthrosis.with a deformation of not more than 20-25%, but the effectiveness of the treatment will be greater when combined with physiotherapy exercises and massage.
Orthopedists and surgeons note the positive effects of water exercises aimed at improving the muscle strength of the legs.
Sanatorium treatment (during a stable remission period) may be recommended for patients with 1-2 degree knee arthrosis, including mud therapy, sauna warm-up, and spas. A special diet is prescribed for overweight patients as obesity is a major factor in the development of knee arthrosis.
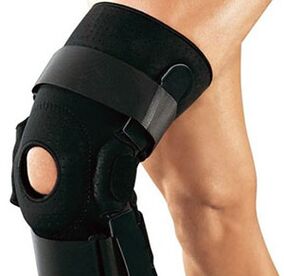
Arthrosis 2 degrees
Treatment of grade 2 arthrosis of the knee joint includes physiotherapy and massage (outside the acute period), special diet, physiotherapy exercises, and medication. It is very important to reduce the load on the injured joint: restrict walking, avoid movements that require knee flexion. In the case of rapidly progressive arthrosis, the use of special orthoses is recommended - orthopedic devices designed to fix the patient's joint and restrict its mobility.
The medication regimen may include the following medications:
- chondroprotectors;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- intraarticular hyaluronic acid injections;
- injections of glucocorticosteroid hormones.
The diet of patients with knee inflammation should include a sufficient amount of collagen-rich food.
This:
- products containing gelling additives (gels, jellies, gels, aspic);
- products containing added pectin;
- fish oil.
Almost all fruits and berries contain essential amino acids and minerals to keep joints healthy and agile, but these foods are worth consuming.limited in diabetics.
Arthrosis 3 degrees
Treatment of grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint is no different from therapy for grade 2 arthrosis.
Due to its ineffectiveness and severe mobility impairment, the patient requires surgical treatment with additional prosthetics of the injured joint.
Folk methods
Consult your doctor before learning how to treat your knee joints with alternative medicine at home. The methods listed below are only allowed in the early stages of grade 1 arthrosis and grade 2 arthrosis.
Nettle and lemon infusion
This infusion should be taken orally 20 to 20 minutes before a meal. A single dose of 50-80 ml.
To prepare the infusion, you must do the following:
- Mix 100 g of dried or fresh nettle leaves with three peeled heads of garlic;
- pass the mixture through a meat grinder;
- add 4 tablespoons of lemon juice;
- mix everything, add 250 ml of boiling water and cover;
- insist for 4 hours.
The duration of treatment in this way is at least 60 days. The infusion should be taken once a day for the first week and twice a day for the next 7 to 10 days. From the third week of treatment, the number of doses should be increased to 3 per day.
Honey ointment for joints
This ointment helps relieve inflammation and reduce pain. The first result is noticeable after one week of use, but should be applied for 30-45 days to achieve a stable result.
To make the ointment, you need to do the following:
- melt 2 tablespoons butter;
- mix the oil with two tablespoons of honey and one tablespoon of 6% apple cider vinegar;
- Put the mixture in the refrigerator to freeze.
Apply this ointment to your knees 2-3 times a day (last time - before going to bed).
Bath with dandelions
For such a bath, a tincture of dandelion roots is used. To prepare it, mix 120 g of crushed dandelion root with 150 ml of vodka and keep in a dark place for a day. Before bathing, the contents of the tank must be poured into water and mixed. It is recommended to take such a bath 1-2 times a week. After the procedure, the knee pain is reduced and the mobility of the joints is gradually restored. The effectiveness of the treatment will be greater if you add 150 g of sea salt enriched in iodine and bromine to the water.
Opinions
- "Only the injection of hyaluronic acid helped with arthrosis. Very good medicine with minimal side effects and high efficiency. I hardly feel any pain in my knee now, though I couldn’t even go down the stairs without help before. "
- "It seems to me that the knee joint is a disease that nothing can cure. You can alleviate the pain a little, but it will still come back. During exacerbations, they are treated with ficus and Jerusalem artichokes. It doesn’t help any worse than the pills, it just doesn’t harm the heart and liver.
- "I was also diagnosed with grade 2 knee arthrosis. The reason was probably overweight (I weighed over 130kg at the time). A salt-free diet, chondroprotectors, anti-inflammatory ointments, and hormonal injections were prescribed for treatment. I did everything as instructed - the arthrosis was completely gone.
Knee osteoarthritis is a severe pathology of the musculoskeletal system that tends to progress rapidly. The treatment regimen should be selected by the treating physician after a comprehensive diagnosis and identification of the extent of the degenerative, dystrophic processes and the deformity of the cartilage and joint surface. The prognosis of treatment depends on adherence to medical prescriptions and timely medical assistance.



















